A gluten free diet (GFD) is a diet that strictly excludes gluten, which is a mixture of proteins found in wheat as well as barley and rye.
A gluten-free diet should be mainly based on naturally gluten-free foods with a good balance of micro and macro nutrients: meat, fish, eggs, milk and dairy products, legumes, nuts, fruits, vegetables, potatoes, rice, and corn are all appropriate components of such a diet.
Wheat is difficult to digest
Humans don’t fully digest wheat. The undigested portions of wheat begin to ferment, producing gas. Icky, belchable, fart-forming gas which may further lead to acidity and indigestion.
Gluten can be inflammatory
If you have a gluten sensitivity, then eating gluten can make your symptoms, like joint pain, worse. Gluten is a pro-inflammatory agent which is rapidly converted to sugar, causing a rise in the body’s insulin levels, causing a burst of inflammation at the cellular level, among other problems.There are reports that gluten can exacerbate arthritis, especially if you already have celiac disease. But, even for people who have non-celiac gluten sensitivities, there may be a connection between eating gluten and swollen joints.
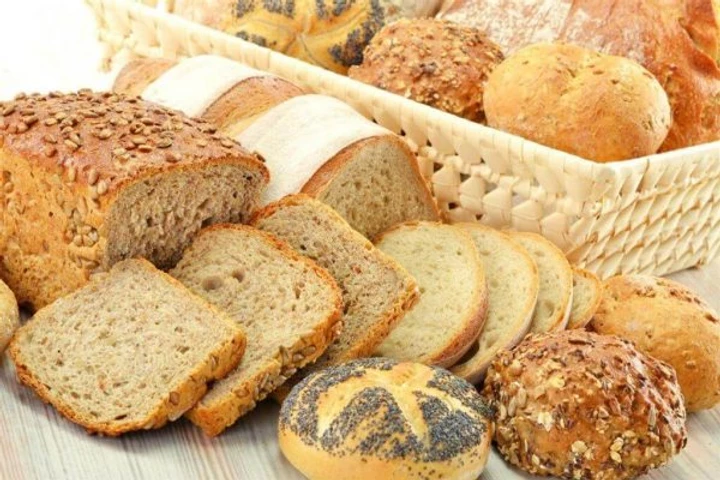

Refined wheat has little nutritional value
Did you know that manufacturers actually have to enrich refined wheat because they’ve taken out all the nutrients? And even then, the wheat’s not that valuable, nutritionally speaking.
Gluten may cause thyroid problems
Gluten can have a negative effect on thyroid disease, and there is research showing that a gluten-free diet can help reduce the antibodies associated with autoimmune thyroid disease.

Gluten may block nutrient absorption
If you do have a gluten sensitivity or celiac disease but you continue to consume gluten, it is possible that your intestinal wall can become inflamed. This condition is sometimes called Leaky Gut Syndrome and can lead to the inability to absorb nutrients from the diet.

